Minimally Invasive
Herniated Disc Surgery
When it comes to spinal pain, whether it is cervical or lumbar, the treatment is always conservative until we reach a point where further conservative treatment is of no value or that conservative treatment would be detrimental to the patient. Under those circumstances, several different treatments can be performed for several different conditions.
For example, patients who have cervical disc herniations or pinched nerves, either from herniated discs or arthritis or some other abnormalities, there are treatments that lead to removal of the herniated discs and fusion of the adjacent segments. However, new technology is allowing the motion preservation technology to be possible, which is in the form of disc replacement, otherwise called disc arthroplasty, in which a device is inserted in the place of the disc that preserves the motion to some extent. We have some experience with this technology in the United States, but not as much as in Europe. It is somewhat more successful in the cervical spine but not as successful in the lumbar spine.
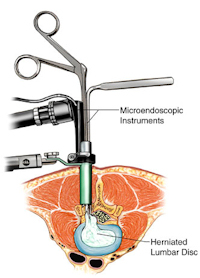
In lumbar surgeries in conditions in which the patients have herniated lumbar discs that are compressing the nerve root itself, a simple laminectomy or diskectomy may suffice, which is actually a removal of part of the lumbar bone that hangs over the disc space and by removing it, it gives room for the nerve to exit. The surgeon can also remove the disc that is herniated or extruded. Sometimes, the joints of the spine can become enlarged and squeeze the nerve. In that case, part of the joints can be sectioned.
In some conditions, patients do not receive the desired result of back pain relief and, therefore, the surgeon and the patient have to understand the mechanism of pain and the pain generated in this condition. Leg pain, or the sciatic type of pain usually occurs from the pinching of the nerve itself as it exits the foramen. The back pain could be of multiple etiologies. It could be from a disc herniation or it could be from the arthritis of the spine or it could be the slippage of one vertebra over the other with abnormal motion due to degenerative disc disease. It could also be from fractures or sometimes congenital abnormalities. In some conditions, a treatment called interbody fusion can be very helpful. This procedure is performed in multiple ways. It can be performed in an open procedure with the removal of lamina and the disc and replacing the disc with either a PEEK device or a titanium device. The interbody fusion is then strengthened with a spinal instrumentation in the form of either the screws in the pedicle and in the vertebra or other forms of instrumentation devices that hold the vertebrae together. The purpose of this is to hold the vertebrae together until the spinal segment fuses.
There are, now, other products that help in the fusion of the spine, called products of bone morphologic proteins (BMP). These chemicals, when used in an appropriate and recommended form, increase the chance of fusion. There are also chemicals like demineralized bone matrix that are also fusion extenders that can be used to help the fusion.
The spinal fusion can be performed both from the posterior level of the spine, called Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion, or through the front of the spine, called Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion , or from the side of the spine, called Lateral Interbody Fusion. The basic principle is the same; that it is to stabilize the spine by the use of spinal instrumentation.
Recently, Minimally Invasive Surgery has revolutionized the surgical world. Not necessarily in neurosurgery, or spine surgery, but in almost every other form of surgery. Minimally invasive surgery means a smaller opening to accomplish the surgical approach and perform the surgery with new technologically advanced instruments that can reach deep and move at different angles. However, it must be understood that minimally invasive surgery could also be maximally destructive. These surgeries are performed under guidance from fluoroscopy and sometimes injury to the nerve root, dura and spinal fluid leak and bleeding may not be controlled through a small opening, and therefore a larger opening and conventional procedure is performed.
Stereotactic Gamma Knife
In treatment of intercranial or brain abnormalities like tumors, cancer, or vascular abnormalities, sometimes a BIOPSY is required to know the exact nature of the condition. At times, the surgeon may perform a conventional biopsy with a slightly larger opening to remove and de-bulk the tumor, depending on the diagnosis. At times, a small piece is removed under a sterotactic guidance which is a guidance controlled by CAT scan of the brain and determining the angle of trajectory to the abnormality and accessing it with a small opening in the skull. After the biopsy, a pathologic analysis is performed to determine whether or not radiation treatment is the answer. Usually, conventional radiation treatment has been performed. But now with Sterotactic Radiosurgery, with multiple robotic armscould be used to administer the dose of radiation with patient placed in a frame, or frameless Sterotactic Radiosurgerycan be performed. In this technique, a pre-determined dose of radiation is administered at a pre-determined level. This radiation effect the tumor or the abnormality without effecting the adjacent normal brain.
To understand these technologies, treatment modalities and conditions, patients should discuss this at length with their physicians and surgeons and educate themselves with written material available at different websites. The links to those websites are included in the educational section.


